DEVELOPING
The city of Antwerp wants to encourage the use of e-mobility to further reduce its emissions. Therefore, the availability of and the connectivity between charging infrastructure and reservation systems needs to be further developed to increase the use and to support sharing opportunities.
Additionally, the aim is to standardly prepare new buildings with parking spaces with all necessary provisions to install a charging infrastructure.
FACTSHEET 08
smart charging infrastructure
Results, findings & lessons learned
More info
|
|
Context & challenges
CONTEXT & CHALLENGES
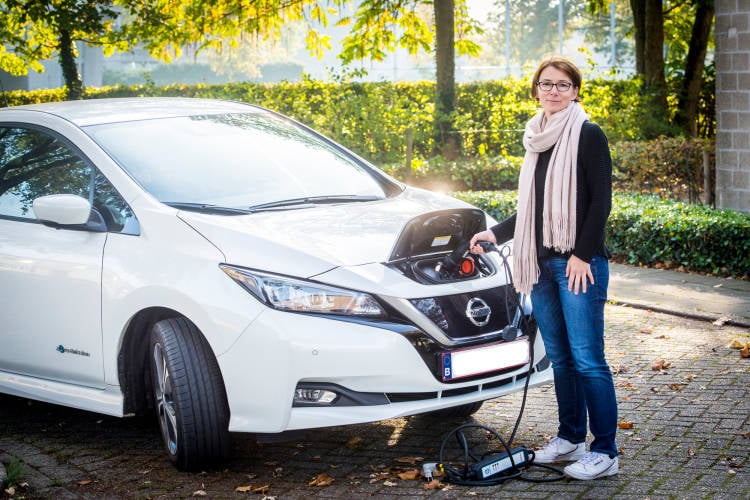
Before CIVITAS PORTIS, the city of Antwerp had ca. 10 publicly accessible charging points spread throughout the city. In the new building code (containing the rules for building and renovating in Antwerp), project developers are required to provide at least one charging point for every 30 parking spaces. The city developed a vision note on e-mobility and is involved in different initiatives to support new concepts of (smart) charging infrastructure and is further mapping options.
Measure level specific objective(s)
- Increase new tailor-made public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles
- Increase off-street charging
- Increase electric vehicle-sharing
- Increase the number of electric vehicles
The implementation was carried out in different stages:
Stage 1:
- Establishment of a new concept of e-car sharing of private stakeholders supported by the city with charging facilities.
- Possibilities to share e-fleet and charging infrastructure of city with citizens and provide an application to facilitate sharing.
- Smart charging solutions when implementing charging infrastructure in P&Rs.
Stage 2:
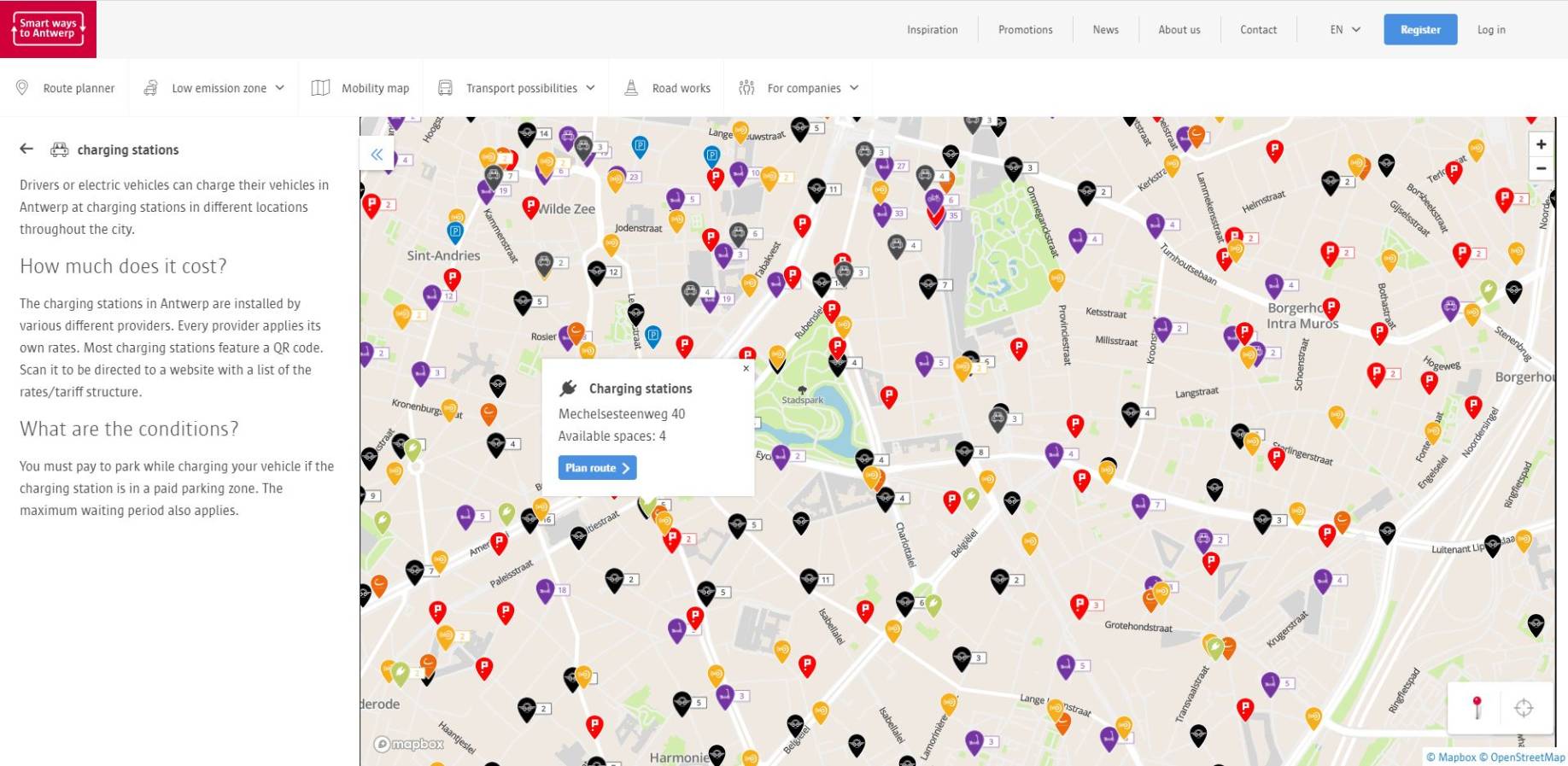
- The charging infrastructure has been added to the smart travel planner of Smart ways to Antwerp
Stage 3:
- Expanding the network of public charging points with support of an online tool to request the installation of e-charging stations
- Adding extra points to strategic locations; based on the increased amount of electric cars (both private, and shared cars)
- Online monitoring dashboard for the city to see the usage of charging points
Stage 4:
- Free use of the charging points for private or car sharing players to encourage the use of e-vehicles
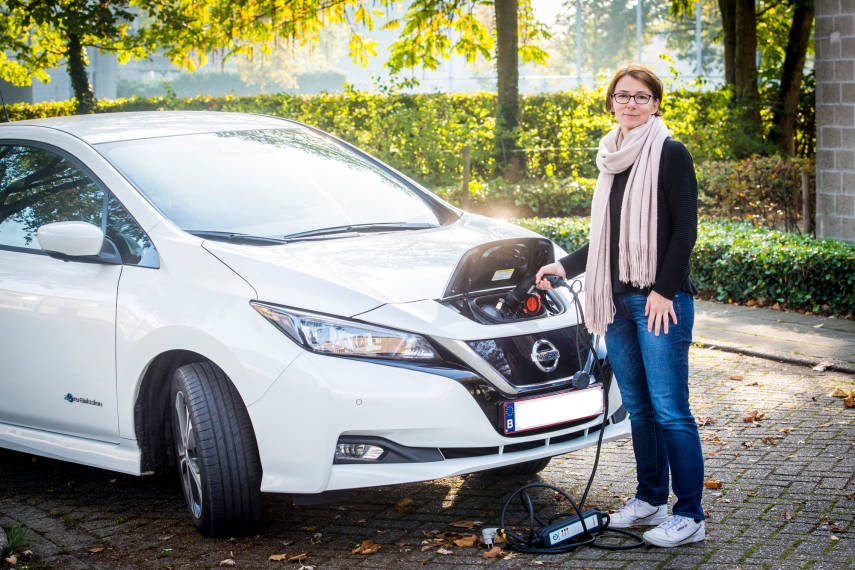


& LESSONS LEARNED
The target of new tailor-made public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles by the end of the project, which is 272, has been reached. The number of off-street charging points was increased by 30 in 2019.
After implementing this measure, these are the main lesson learnt, important for future sustainable mobility strategies:
• Key lesson 1: There are still a lot of mental barriers and need for awareness raising which need to be overcome when it comes to electric vehicles. However, people are more aware of e-mobility and of electric charging possibilities. Cities should not underestimate these barriers and need to have attention for ‘soft’ measures next to infrastructure.
• Key lesson 2: Legislation could benefit from an update when it comes to the implementation of charging infrastructure (location, reservation system…). Cities need to run parallel with the roll-out of infrastructure, together with a legislation trajectory in order to facilitate electric car use.
• Key lesson 3: Cities have to invest in training and time to follow up internally in the city. There are a lot of factors which play a role (relationship with service providers, links with other city departments, rapid evolvement in the market…) and a dedicated project leader in the city is necessary.

www.slimnaarantwerpen.be
www.antwerpen.be
More info about CIVITAS PORTIS
can be found on the website civitas.eu/portis

DEVELOPING
The city of Antwerp wants to encourage the use of e-mobility to further reduce its emissions. Therefore, the availability of and the connectivity between charging infrastructure and reservation systems needs to be further developed to increase the use and to support sharing opportunities.
Additionally, the aim is to standardly prepare new buildings with parking spaces with all necessary provisions to install a charging infrastructure.
FACTSHEET 08
smart charging infrastructure
Results, findings & lessons learned
More info
Context & challenges
CONTEXT & CHALLENGES
Before CIVITAS PORTIS, the city of Antwerp had ca. 10 publicly accessible charging points spread throughout the city. In the new building code (containing the rules for building and renovating in Antwerp), project developers are required to provide at least one charging point for every 30 parking spaces. The city developed a vision note on e-mobility and is involved in different initiatives to support new concepts of (smart) charging infrastructure and is further mapping options.
Measure level specific objective(s)
- Increase new tailor-made public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles
- Increase off-street charging
- Increase electric vehicle-sharing
- Increase the number of electric vehicles

The implementation was carried out in different stages:
Stage 1:
- Establishment of a new concept of e-car sharing of private stakeholders supported by the city with charging facilities.
- Possibilities to share e-fleet and charging infrastructure of city with citizens and provide an application to facilitate sharing.
- Smart charging solutions when implementing charging infrastructure in P&Rs.
Stage 2:
- The charging infrastructure has been added to the smart travel planner of Smart ways to Antwerp
Stage 3:
- Expanding the network of public charging points with support of an online tool to request the installation of e-charging stations
- Adding extra points to strategic locations; based on the increased amount of electric cars (both private, and shared cars)
- Online monitoring dashboard for the city to see the usage of charging points
Stage 4:
- Free use of the charging points for private or car sharing players to encourage the use of e-vehicles

& LESSONS LEARNED
The target of new tailor-made public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles by the end of the project, which is 272, has been reached. The number of off-street charging points was increased by 30 in 2019.
After implementing this measure, these are the main lesson learnt, important for future sustainable mobility strategies:
• Key lesson 1: There are still a lot of mental barriers and need for awareness raising which need to be overcome when it comes to electric vehicles. However, people are more aware of e-mobility and of electric charging possibilities. Cities should not underestimate these barriers and need to have attention for ‘soft’ measures next to infrastructure.
• Key lesson 2: Legislation could benefit from an update when it comes to the implementation of charging infrastructure (location, reservation system…). Cities need to run parallel with the roll-out of infrastructure, together with a legislation trajectory in order to facilitate electric car use.
• Key lesson 3: Cities have to invest in training and time to follow up internally in the city. There are a lot of factors which play a role (relationship with service providers, links with other city departments, rapid evolvement in the market…) and a dedicated project leader in the city is necessary.
www.slimnaarantwerpen.be
www.antwerpen.be
More info about CIVITAS PORTIS
can be found on the website civitas.eu/portis
